- Oct 21, 2018
- admin
- 0
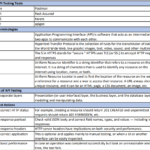
What are the differences between SOAP and REST?
SOAP is the heavyweight choice for Web service access. It provides the following advantages when compared to REST:
- SOAP is not very easy to implement and requires more bandwidth and resources.
- SOAP message request is processed slower as compared to REST and it does not use web caching mechanism.
- WS-Security: While SOAP supports SSL (just like REST) it also supports WS-Security which adds some enterprise security features.
- WS-AtomicTransaction: Need ACID Transactions over a service, you’re going to need SOAP.
- WS-ReliableMessaging: If your application needs Asynchronous processing and a guaranteed level of reliability and security. Rest doesn’t have a standard messaging system and expects clients to deal with communication failures by retrying.
- If the security is a major concern and the resources are not limited then we should use SOAP web services. Like if we are creating a web service for payment gateways, financial and telecommunication related work, then we should go with SOAP as here high security is needed.
REST is easier to use for the most part and is more flexible. It has the following advantages when compared to SOAP:
- Since REST uses standard HTTP, it is much simpler.
- REST is easier to implement, requires less bandwidth and resources.
- REST permits many different data formats whereas SOAP only permits XML.
- REST allows better support for browser clients due to its support for JSON.
- REST has better performance and scalability. REST reads can be cached, SOAP based reads cannot be cached.
- If security is not a major concern and we have limited resources. Or we want to create an API that will be easily used by other developers publicly then we should go with REST.
- If we need Stateless CRUD operations then go with REST.
- REST is commonly used in social media, web chat, mobile services and Public APIs like Google Maps.
- RESTful service returns various MediaTypes for the same resource, depending on the request header parameter “Accept” as application/xml or application/json for POST and /user/1234.json or GET /user/1234.xml for GET.
- REST services are meant to be called by the client-side application and not the end user directly.
- ST in REST comes from State Transfer. You transfer the state around instead of having the server store it, this makes REST services scalable.